The Core Activities Behind Every Efficient Warehouse
Warehouse operations represent the daily activities that keep goods flowing smoothly from receiving to shipping.
These operations define how fast orders are processed, how accurate inventory remains, and how efficiently space,
equipment, and labor are used. For small and medium-sized warehouses, strong operational discipline is the key to
preventing delays, stock inaccuracies, bottlenecks, and customer dissatisfaction.
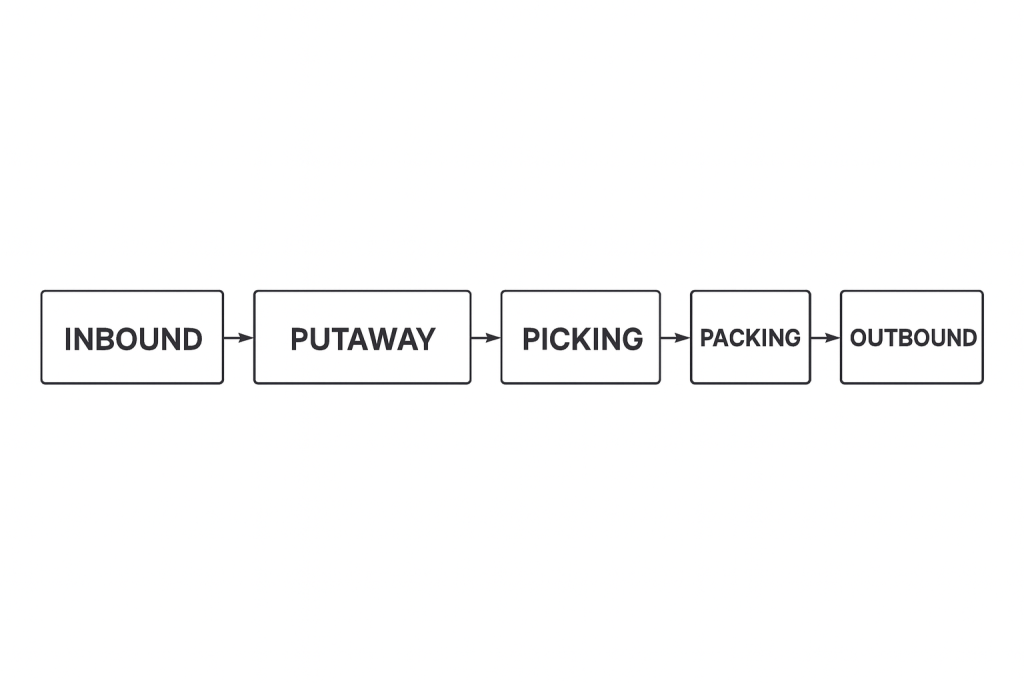
A well-organized warehouse must coordinate multiple processes: inbound, putaway, storage, picking, replenishment,
packing, and outbound. Each activity has its own rules, KPIs, and best practices. When operations are aligned and
standardized, the warehouse becomes predictable, fast, and scalable — regardless of size.
The sections below provide practical guides, tools, and explanations that help teams understand and optimize every
aspect of warehouse operations. Each topic is designed for real-world use and is easy to apply in SMEs.
Create process diagrams
easily and quickly
Generate clear warehouse process diagrams in
minutes using simple online tools.
Warehouse Operations – Key Processes Explained
Warehouse operations are the foundation of efficient supply chain management.
Optimizing pallet loading
Provides strategies for maximizing pallet space while ensuring safe and stable stacking.
How to Operate a Warehouse Without a WMS
Whether due to cost, complexity, or business scale, many small and medium-sized warehouses operate without a WMS.
Warehouse Operations – FAQ
Need quick answers?
See the full “Warehouse Operations – FAQ” page.
Warehouse KPIs-Performance and Service Quality
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in a warehouse are essential for evaluating operational efficiency, workforce productivity, and service quality.
Warehouse Budget Planning
A warehouse budget is a key management tool that helps organizations control operational costs, plan future investments, and assess performance efficiency.
Returns Management – Practical Guide
Unlike standard inbound flows, returns require additional control points, decision logic, and traceability
