1. The Role of Shelving in Warehouse Organization
Shelving systems are essential for storing small items, components, spare parts, tools, documents, slow movers,
and all products that do not require pallet racking. A well-designed shelving layout improves stock visibility, reduces
searching time, and supports fast picking routines. For small and medium warehouses, shelving is one of the most
cost-effective solutions for organizing inventory and increasing productivity without large investments.
Warehouse teams often ask which type of shelving is best for their operation or how much weight each system can support.
The right choice depends on product size, turnover frequency, operator access, and the level of flexibility required.
Below is a clear and practical guide to the most common shelving systems used in warehouses.
2. Shelving vs. Racking – Understanding the Difference
Before choosing the right system, it is important to distinguish between:
Shelving
- for small items
- hand-picked
- lower height
- lightweight or medium-weight
- high visibility
- used in spare parts, ecommerce, tools, workshops
Racking
- for pallets
- requires forklift access
- heavy-duty
- vertical optimization
- used for full pallet storage
Shelving is not a weaker version of racking — it is a different category, designed for manual picking and high visibility.
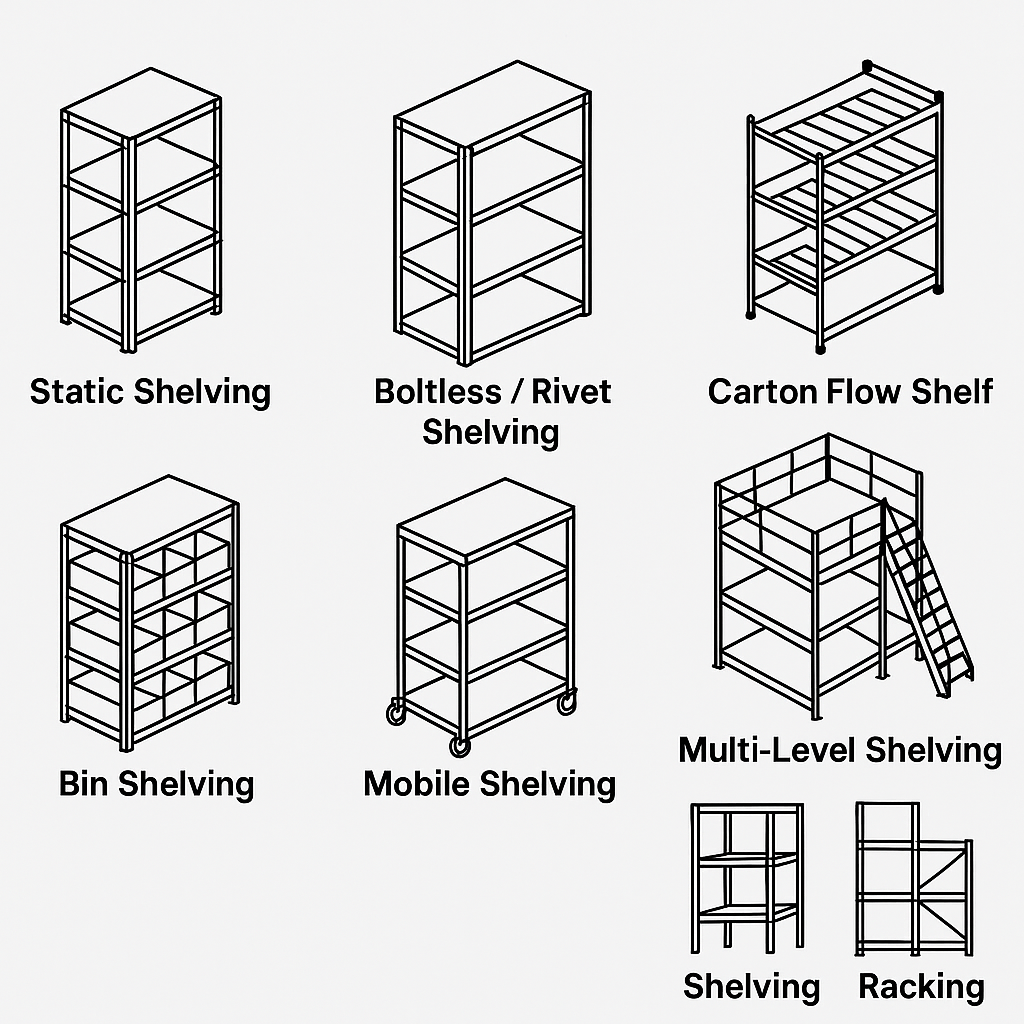
3. Main Types of Shelving Used in Warehouses
3.1 Static Shelving (Fixed Shelving)
The most common and cost-effective solution.
Best for: slow movers, documents, tools, small spare parts.
Advantages:
- low cost
- easy to install
- stable and simple to maintain
- high visibility
Limitations:
- fixed structure (no mobility)
- not suitable for heavy loads
3.2 Boltless / Rivet Shelving
Very popular due to flexibility and fast installation.
Used in ecommerce, workshops, service departments.
Advantages:
- no tools required
- modular and adjustable
- ideal for mixed products
Limitations:
- limited load capacity per shelf
3.3 Bin Shelving (Small Parts Shelving)
Designed for small SKU storage using plastic bins, trays, or dividers.
Advantages:
- excellent SKU separation
- high picking accuracy
- ideal for spare parts
Limitations:
- reduced visibility if bins are deep
- requires labeling discipline
3.4 Mobile Shelving (Compact Shelving)
Shelving units mounted on rails to save space.
Advantages:
- maximizes density
- reduces floor footprint by 40–50%
Limitations:
- slower access
- suitable only for low/medium frequency items
3.5 Carton Flow Shelving (Gravity Shelving)
Uses rollers that allow items to slide from back to front.
Advantages:
- FIFO automatic
- high picking speed
- excellent for fast movers
Limitations:
- higher cost
- requires proper carton quality
3.6 Multi-Level Shelving Systems
Walkways or mezzanines added above shelving rows.
Advantages:
- doubles usable space
- suitable for small items and ecommerce
Limitations:
- requires safety measures
- limited for heavy products
4. Choosing the Right Shelving System
Warehouse managers often ask which shelving type is best for SMEs.
The answer depends on:
- SKU variety
- product size and weight
- picking frequency
- available height and floor area
- need for expansion
General rule:
- Fast movers → carton flow or easily accessible static shelving
- Medium movers → standard adjustable shelving
- Slow movers → upper shelves or mobile shelving
5. How Shelving Integrates with Warehouse Layout
Shelving placement affects:
- walking distance
- picking routes
- inventory control routines
- safety
- replenishment cycles
Shelving should always be grouped logically, with wide aisles for access and clear labeling for easy SKU identification.
6. FAQ
Should shelving be color-coded?
Yes — using contrasting colors helps operators navigate faster and reduces search time.
How often should shelving be reorganized?
Every 6–12 months, or after major assortment changes.
Can shelving be used with a WMS?
Absolutely — bin locations can be scanned and mapped just like pallet locations.
